SolderTip #45: Manual Soldering vs Wave Soldering
Blog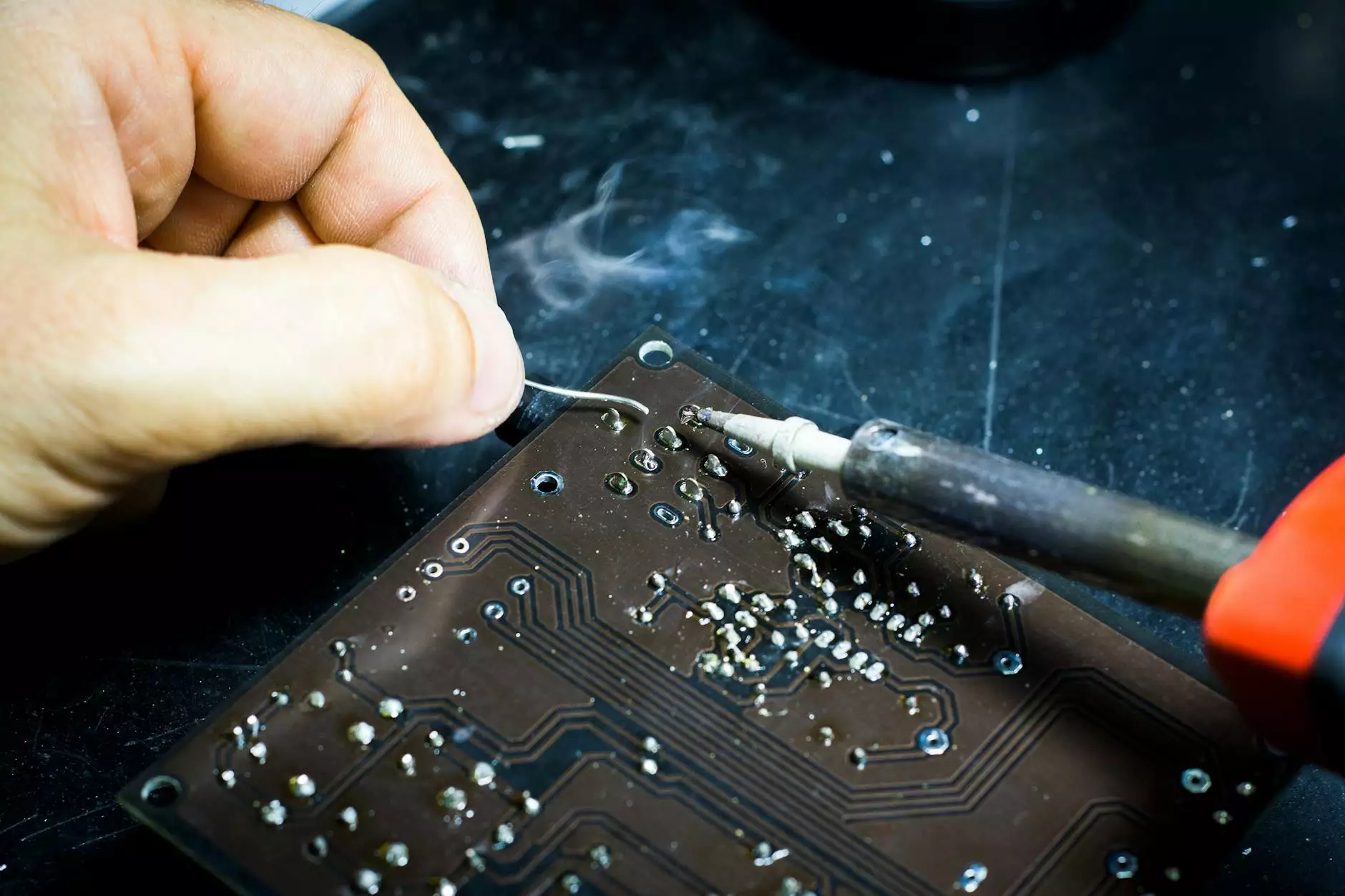
The Importance of Choosing the Right Soldering Technique in the Electronics Industry
In the world of electronics manufacturing, having the proper soldering technique can greatly impact the quality and reliability of the finished product. Two commonly used methods are manual soldering and wave soldering. Understanding the differences, benefits, and drawbacks of both techniques is crucial for any professional in the industry.
What is Manual Soldering?
Manual soldering is a process where solder is applied to the joints and components on a printed circuit board (PCB) using a soldering iron or a soldering station. This technique requires a skilled operator who meticulously solders each connection individually.
Advantages of Manual Soldering
- Precision: Manual soldering allows for precise control over the soldering process, ensuring accurate and consistent connections.
- Flexibility: With manual soldering, operators can easily navigate complex PCB layouts and reach tight spaces that automated machines might struggle with.
- Repairability: Manual soldering facilitates easier repairs or modifications since individual soldered connections can be isolated and modified without affecting the entire board.
Disadvantages of Manual Soldering
- Time-consuming: Manual soldering is a labor-intensive process that requires time and effort, especially when dealing with intricate and densely-populated PCBs.
- Potential for human error: The quality of manual soldering heavily relies on the skill and experience of the operator, which can introduce the risk of human error and inconsistent soldering quality.
- Inconsistent thermal management: Achieving consistent heat distribution across multiple solder joints can be challenging, potentially leading to uneven solder connections and compromised reliability.
What is Wave Soldering?
Wave soldering is an automated method of soldering PCBs. It involves passing the entire board over a wave of molten solder, which forms a perfect and uniform solder connection with the components.
Advantages of Wave Soldering
- Efficiency: Wave soldering can significantly reduce the time required for soldering, making it ideal for high-volume production.
- Consistency: The automated process ensures uniform solder connection quality across the entire PCB, eliminating human error and inconsistencies.
- Thermal management: The controlled heating profile of wave soldering minimizes the risk of thermal stress on components and enables reliable solder connections.
Disadvantages of Wave Soldering
- Lack of flexibility: Wave soldering machines are optimized for specific board layouts, which might limit the use of this technique for complex or non-standard PCB designs.
- Inability to handle certain components: Some delicate or heat-sensitive components may not withstand the high temperature required for wave soldering, making manual soldering the preferred option.
- Cost: Setting up and maintaining wave soldering equipment can be expensive, especially for smaller-scale operations.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Needs
When deciding between manual soldering and wave soldering, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of your project and the resources at your disposal. Factors such as production volume, board complexity, component types, and desired solder quality should all be taken into account.
Factors to Consider:
- Production Volume: For small-scale or customized production runs, manual soldering offers greater flexibility and cost-efficiency. In contrast, wave soldering is often more suitable for large-scale manufacturing.
- Board Complexity: If your PCB design involves intricate layouts, tight spaces, or non-standard component orientations, manual soldering might be the better choice for ensuring precise connections.
- Component Types: Delicate or heat-sensitive components, such as surface-mount technology (SMT) devices, may require the gentler heat application of manual soldering.
- Solder Quality: If your project demands consistent and reliable solder connections, wave soldering's automated process can offer superior results.
Conclusion
In summary, choosing between manual soldering and wave soldering depends on several factors, such as production volume, board complexity, component types, and desired solder quality. Both techniques have their own advantages and disadvantages, and each finds its place in the electronics industry.
Ultimately, finding the right balance between manual and automated soldering methods is crucial to meet project requirements efficiently and deliver high-quality electronic products.
If you need expert guidance or have specific questions related to soldering techniques, our team at Luxury Ride Dubai is here to assist you. Contact us now to learn more!